I was on the birth control pill for ten years. I knew that it could cause blood clots in women over 35 who smoked. I wasn’t over 35 and I didn’t smoke. That was all I thought I needed to know. Then I had a stroke. It was caused by the pill and a genetic clotting disorder I never knew I had. In fact, I didn’t know there was such a thing as clotting disorders or that I could have one or that in combination with hormonal birth control, it could kill me. And I certainly had no idea what the symptoms of a blood clot were.
What Do We Know? Not Too Much, It Appears
When I began to do research for my thesis, I wanted to know if it was just me or if other women who took the pill were also unaware of clotting disorders and of the symptoms of a blood clot. Spoiler: I wasn’t alone in my ignorance.
I surveyed over 300 women who had taken birth control pills. Among other things, I wanted to know:
- What did women know about the risks associated with the pill?
- Were they aware of clotting disorders?
- Did they know the symptoms of a blood clot?
Survey Results
Neither Women Nor Their Doctors Understand Risks for Blood Clots
The results of the survey showed that women do not clearly understand the risks involved with taking birth control pills. Many of them believe that certain risks are only associated with being over 35 years of age and/or smoking. This is not surprising given that only a little over half said their doctor discussed the risks with them before giving them a prescription. And for a majority of the women, their doctor never discussed other birth control options with them.
Most of the women were asked about their family history before being given a prescription, but fewer than half of their doctors actually discussed it with them, and fewer than a third of the women actually read the risk information that accompanies their prescriptions. That’s not surprising given how dense and misleading the pharmaceutical companies have made risk communication.
When asked whether they were familiar with the symptoms of a blood clot, most women (60.5%) admitted that they were not. Eight women responded that they had learned the symptoms because a family member or friend had a blood clot, and two participants said they had actually had blood clots. One stated, “When I experienced chest pain and did research online. It turned out that I had pulmonary embolisms (while on BCP- birth control pills).” Only 6 out of 311 women reported learning about the symptoms of blood clots from their doctor. Ironically, more women knew someone who had a clot.
At the end of the survey, the participants were invited to share anything further about their experience on the pill. Here are some of their answers:
My experience on birth control pills, the Nuvaring, or Depo-Provera all proved to be horrendous… I think birth control pills came straight from hell and I hate, hate, hate it. I would rather undergo Chinese water torture daily thank take birth control, and that is the God’s honest truth… My fertility has been affected forever by my under informed choice to go on birth control, and by the irresponsible doctors who encouraged me to switch methods rapidly “until I found what worked for me.”
I’ve had two different GYNs give me completely contradictory information about the side effects and dangers of BCPs… Overall, I’m surprised at how little doctors seem to know about female BCP- I haven’t experienced this amount of ambiguity with any other medical specialty or problem.
I was shocked- and grateful- when I finally found a doctor who discussed alternatives with me, suggested a wide variety of reading, and let me do my own research and make my own decision before wiring[sic] a prescription. After doing the reading, there is no way I will ever take another birth control pill in my life. Every other doctor I had acted like it was giving out Altoids…
I think they’re too often the first option doctors prescribe for reasons other than birth control. That’s frustrating. They’re not a magic pill and some doctors seem to think they are.
The bottom line is that most women do not fully understand the risks involved with taking birth control pills and they are not familiar with the symptoms of a blood clot.
At my thesis defense, when I mentioned that most women (over 60%) did not know the symptoms of a blood clot, my advisor asked, “Well, I don’t think that’s so unusual. Do you think most people know what the symptoms of a blood clot are?”
“No, but I think people who have been prescribed a medication that greatly increases their risk of blood clots should be informed of the symptoms,” I responded.
Who Is Responsible?
This is a simple question with a complicated answer. Who is responsible for making sure women who use hormonal contraceptives, especially women who are at a much higher risk for blood clots, understand the symptoms and when to get help? Is it the responsibility of the doctor who prescribed the medication? Or is it the responsibility of the pharmaceutical company to provide clearer information? Or is it the responsibility of the patient?
From my personal experience, I now know that I cannot trust my doctor to always make the right diagnosis and provide the right treatment. Most of their information comes from the pharmaceutical industry who have clearly demonstrated that they put profit first. And our research is showing that their information is not correct. Therefore, I cannot rely on the drug companies to make sure they provide me with accurate and straightforward information about their medications.
So that leaves me. And you. Until we demand a system that puts patients first, a system of health and transparency, we have to put ourselves firsts. How? We do that by listening to our bodies, doing the research, and learning to trust our intuition. That may mean we have to disagree with our doctors. That may mean we have to ask for a second opinion. That may mean we have to insist on being heard. We can’t be afraid of offending someone or “rocking the boat.” We can’t be afraid of being considered hysterical or melodramatic. We can no longer sit back and hope others are making the best decisions for us. We have to educate ourselves. We must be our own advocates. Our lives depend on it.
And we can start by learning the symptoms of a blood clot.
What Are the Symptoms of Blood Clots?
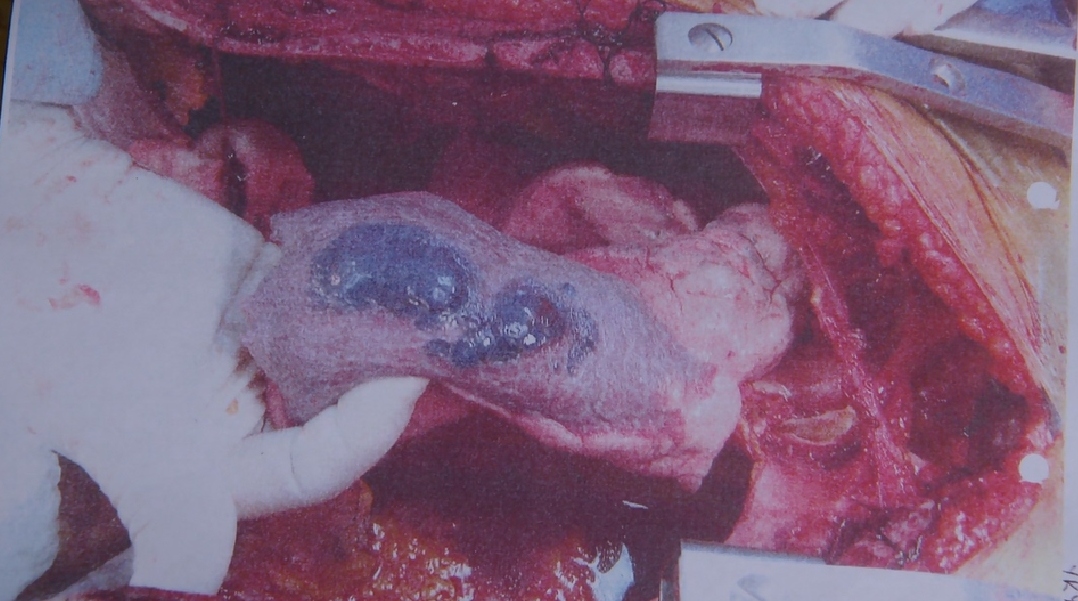
Blood clot in leg:
- swelling
- pain
- tenderness
- an unusually warm sensation in the affected area
- an unusually cold sensation in the affected area (this is per our research, more details to follow)
- pain in your calf when you stretch your toes upward
- a pale or bluish discoloration
Blood clot in chest:
- sudden shortness of breath that can’t be explained by exercise
- chest pain, may feel like extreme heart burn
- palpitations, or rapid heart rate
- breathing problems
- coughing up blood
- dizziness (per our research)
- uncharacteristic fatigue (per our research)
Blood clot in the brain:
- severe headache
- loss of speech
- numbness or tingling of limbs
- difficulty seeing or changes in vision
- difficulty speaking or finding words
For more information about blood clots, especially in conjunction with hormonal contraceptive use, click here.












Kerry, this is a great article. I think your thought process was pretty typical as an under-35, non-smoker, and one that was engineered to some degree. I’m writing about that for an upcoming post. Thanks for the added inspiration!
I look forward to reading your thesis.