Severe Adverse Reactions Include Vitamin D Deficiency and Autoimmunity
Hormones Matter researchers discovered that, inter alia, severe adverse reactions to any of the surveyed drugs trigger significant but varying autoimmune responses. Moreover, the research revealed an underlying consistency involving all reviewed drugs: vitamin D deficiency.
Vitamin D Helps Regulate the Adaptive Immune System
The adaptive immune system comprises the body’s intricate network of antibodies and special types of white blood cells (called sensitized lymphocytes ) to thwart new and previous invaders including viruses, bacteria, and drugs. When the adaptive immune system is not strong enough to endure external disruptions such as severe side effects of drugs, it can go awry by signaling antibodies and sensitized lymphocytes to attack healthy cells. This response is called autoimmunity—when the adaptive immune system’s cells do not recognize previous invaders and designate healthy cells as those invaders. In other words, the body’s immune cells attack its own healthy cells.
Scientific research over the past three decades solidifies the connection between vitamin D and autoimmunity. Vitamin D plays an integral role in the regulation of the adaptive immune system. Adequate vitamin D in our bodies can protect us from autoimmunity because adaptive immune cells contain vitamin D receptors (VDRs). These receptors are attached to the surface of the adaptive immune system’s antibodies and sensitized lymphocytes. The VDRs act as “gate keepers” by signaling what external substances, e.g., components of medications, can enter a cell. The VDRs must be replete with vitamin D to effectively regulate adaptive immunity. When the VDRs receive adequate amounts of vitamin D, they enable the adaptive immune system to function properly by attacking new and previous invaders.
When the VDRs attached to the adaptive immune system’s cells do not contain sufficient vitamin D to attack invaders, autoimmunity may kick in, causing the death of healthy immune cells. Thus, low vitamin D levels can lead to autoimmune diseases including thyroid disorders such as Hashimoto’s and demyelinating diseases including multiple sclerosis (MS).
Vitamin D and Hashimoto’s Autoimmune Thyroid Disease
The Real Women, Real Data research also uncovered another consistency among severe adverse reactions to the reviewed drugs: Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, an autoimmune disease caused by abnormal cells constantly assaulting the thyroid gland
.
Vitamin D receptors are present in the thyroid as well as the pituitary, the pea-shaped gland that controls the thyroid. Not surprisingly, low levels of serum vitamin D have been linked to Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, according to recent Turkish medical research:
Published in a 2013 issue of the journal Endocrine Practice, a study conducted at a training and research hospital in Ankara demonstrated that serum vitamin D levels of female chronic Hashimoto’s patients were significantly lower than healthy subjects. Furthermore, the researchers discovered a direct correlation between serum vitamin D levels and thyroid volume as well as an inverse correlation to the antibodies involved in the thyroid.
Researchers at Medeniyet University’s Goztepe Education and Research Hospital in Istanbul learned that 92 per cent of their 161 Hashimoto’s thyroiditis cases had serum vitamin D levels lower than 30 ng/mL (12 nmol/L), a value characterized as “insufficient.” Published in a 2011 issue of the journal Thyroid, the study reports an association between vitamin D insufficiency and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
Vitamin D and Demyelinating Disorders
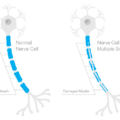
Another disturbing outcome of the Real Woman, Real Data research is the reporting of neurological and neuromuscular symptoms, many which of are consistent with demyelinating disorders such as MS, an autoimmune disease. The development of MS occurs when a poorly functioning, adaptive immune system gradually attacks the protective covering of the nerve cells (called the myelin sheath) of the brain and spinal cord. This potentially debilitating process is called demyelination.
Scientific—primarily epidemiological—research indicates an association between vitamin D levels and the risk of developing a demyelinating disorder such as MS. VDRs exist on nerve cells and the myelin sheath. When the VDRs receive adequate amounts of vitamin D, they help protect the integrity of the myelin sheath. However, when the VDRs do not contain sufficient vitamin D, autoimmunity may occur, resulting in the death of healthy nerve cells. Numerous clinical trials are underway to assess the connection between vitamin D status and the likelihood of developing demyelinating disorders.
Low Vitamin D: The Chicken or the Egg?
The connection between low vitamin D status and the development of autoimmune disease is genuine. However, medical research has not yet determined if vitamin D deficiency plays a role in the development of autoimmune disease, if low vitamin D levels are a consequence of the disease itself, or if vitamin D deficiency acts as both a cause and effect. The authors of the aforementioned 2013 Hashimoto’s study concluded,
“Finally, our results suggested that there may be a causal relation between vitamin D deficiency and development of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. On the other hand, there might be a possible relation between severity of vitamin D deficiency and progression of thyroid damage. However, further studies are needed especially about the effects of vitamin D supplementation on prevention and/or progression of autoimmune thyroid disease.”
Proactive Protection against Severe Adverse Reactions
We could wait years (or decades) to garner the results of further scientific studies and clinical trials to define the exact relationship between vitamin status and severe adverse reactions to vaccines and medications that culminate in autoimmune disorders. Or we could be proactive by taking daily vitamin supplements and enjoying moderate sunlight exposure to increase our vitamin D levels.
It is imperative to take enough vitamin D3 so this essential nutrient will be stored in your cells to help regulate your immune system. The greater your serum vitamin D level (easily obtained from a simple blood test called 25(OH) D, the more likely you will benefit from a stronger immune system that protects your body’s cells from attacking one another.
No one wants to endure severe adverse reactions to drugs such as Gardasil and Lupron, let alone an autoimmune disease. Attaining and maintaining adequate supplementation provides a safe, easy, and inexpensive approach to improved preventive health. By empowering yourself with adequate vitamin D, you may reap the benefits of avoiding disease and enjoying better quality of life.
Copyright © 2013 by Susan Rex Ryan. All rights reserved.
This article was published previously on Hormone Matter in September 2013.
We need your help.
Hormones Matter needs funding now. Our research funding was cut recently and because of our commitment to independent health research and journalism unbiased by commercial interests, we allow minimal advertising on the site. That means all funding must come from you, our readers. Don’t let Hormones Matter die.