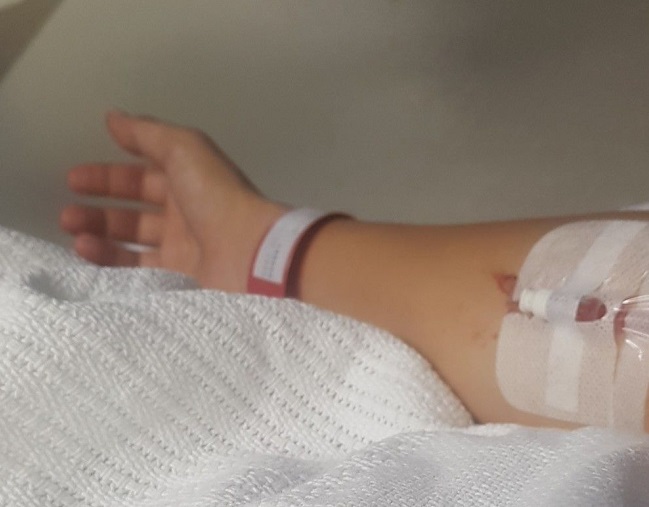
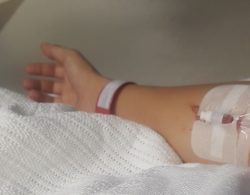
Hi, my name is Jess, I have two children, whom I gave birth to at age 17 and 19. This saved me in ways I could write a book about. I also had one miscarriage. Members of my family have a history of gynecological problems and some of them struggle with fertility. I also was at high risk for hormonal problems due to my strong family history. What I did not know, was just how limited doctors’ understanding of menstrual and hormone problems was. For every problem I presented with, hormonal birth control and painkillers were the answer. When those didn’t work, surgery. I had 10 operations in the span of a few years, until finally and out of desperation, I had a total hysterectomy in my twenties. I cannot help but wonder if the Depo Provera prescribed to me after the birth of my second child was somehow the root of my illnesses and all of the other prescriptions for hormonal birth control added and worsened my pain. It seems like I was in vicious cycle. Here is my story.
Hormonal Birth Control, Pain, and the Long List of ER Visits and Unsuccessful Surgeries
Depo Provera: The Beginning of My Pain
At my 6-week post birth check-up for my 2nd child, the doctor I recommended that I go on the Depo Provera shot to prevent any further pregnancies. So, I did. In September 2013, after two more shots of the Depo Provera, I started having “a period” that lasted 7 months! After multiple doctors’ visits, lots of medications and tests, I was referred to my first specialist, a gynecologist.
Operation 1. In April 2014, at 20 years old, I had my first gynecological surgery: a hysteroscopy, along with a D&C and a Mirena inserted to stop the “period” I was having. The Mirena was also for birth control.
The Mirena Chronicles: More Pain and Ruptured Cyst
For the next 8 months, I had extremely irregular periods, unusual pain, and contemplated having the Mirena removed. The specialist recommended that I keep it in and see if it settles. Intercourse was painful, and after, I was guaranteed to wake up bleeding the next day. My pain became unbearable and after I had an ultrasound, they found I had a cyst on my left ovary. I was given prescription pain relief and was told they would do another ultrasound in 4-6 weeks. That didn’t happen because the pain was slowly getting worse. After two more visits to the emergency department with more pain medication, I was still told that we needed to take a wait and see approach. My health was declining. I lost 7 kilograms in 3 weeks from feeling so unwell.
Then one day I collapsed with severe sudden pain. I went to the hospital straight away when another ultrasound revealed the cyst on my ovary had ruptured. I was told I needed to undergo surgery.
Operation 2. I had a laparoscopy, so they could clean out the mess from the ruptured cyst.
Irregular Bleeding, Another Cyst, Endometriosis, and Still, Mirena is the Solution
A couple months went by and my pain once again returned. I still was having irregular bleeding and was still guaranteed to be bleeding after having intercourse. It was like déjà vu. Unfortunately, I was back on pain killers and an ultrasound revealed another ovarian cyst. The pain was often unbearable. Off to the emergency department again. Multiple pain medications didn’t seem to be working and I was told I need to deal with it as there was nothing they could really do. I thought “Are you serious?!?! Why the hell won’t you help me?!?!” I was a mess.
At every hospital visit, I got the “Oh you are on a lot of bad medication; you shouldn’t take so much.” So I would ask “can you please do something? I don’t want to keep shoveling pills down my throat!!”. However, every time the answer seemed to be “here are some more medications for your pain because we can see you’re in a lot of pain and your vital signs are showing you are in a lot of pain”. This wasn’t providing any sort of solution to fix my pain and being told to suck it up and get over it, by one doctor, didn’t help either. I couldn’t help but feel depressed and severely anxious every time I needed to go to the emergency department. I was in so much pain I didn’t know what to do. When did I become a person who needed multiply prescription medicines to control the pain enough that I could function semi-normally? At one point, I weighed only 48 kilograms. I had lost 10 kilograms. I could barely eat. Every day I tried to stay positive, but it was so hard being consumed in pain 24 hours, 7 days a week.
Operation 3. I had another laparoscopy on the 1st of May 2015, where I had the cyst removed from my left ovary. This is when they told me I had some endometriosis. They inserted another Mirena as a treatment option. It seems as though, birth control and pain killers are the only answers that they have.
Rinse and Repeat and Repeat and Repeat: More Hormonal Birth Control and More Surgeries
By September 2015 the same thing happened again, another large cyst, given away by the extreme pain and accompanied by the irregular bleeding! Another round of multiple hospital visits and admissions, I was again put on really strong pain killers and we discussed treatment options. I was prepped for a procedure called an aspiration and drainage, but my bowel and bladder were collapsed over, and they couldn’t perform it.
Operation 4. On the 24th September 2015, I had another laparoscopy. Another large cyst and more endometriosis were removed. After surgery, I was placed on a different birth control pill, along with the Mirena IUD, as a treatment option for the reoccurring cysts and endometriosis.
By January 2016 my pain had once again come back, and I was admitted to hospital. The result showed that I had another cyst on my left ovary. (Seriously, WTF!!! So many more tears). They told me they didn’t want to do any more operations on me, and I sure as hell didn’t want anymore. I was now 22 and felt like I was failing as a mum and person because I was always so consumed in pain. There were days where I couldn’t even leave the house. I had the Mirena removed again and was once again on pain killers. I was put on a hormonal birth control pill; a much higher dose, and we all prayed this would give me relief.
I had started to build up a resistance to any sort of pain relief. It felt like I was constantly going to the emergency department and was always sent home with more pain killers. Most of the time, the same ones I already took daily. I was going because my pain was so out of control, everyone around me was telling me to go get help, including my GP because I could barely function. Why were they sending me home on the same pain killers that didn’t control my pain? This affected my emotional state further. Some nurses, doctors and people were really kind to me, and others were extremely nasty and made me feel guilty for being in so much pain. I really didn’t want to be sent home again with no solution. “We must figure something out, please stop doing this to me!!! It has happened too many times!”
By March 2016, I was still in chronic pain and on even more daily medications. I had another ultrasound which reveal that I still had another large cyst in my left ovary. It also showed that I had nephrocalcinoisis (calcium build-up) and a small cyst in one of my kidneys, I was told this could be from long term use of pain medication but not exclusively. My jaw dropped. I had to travel to see a kidney specialist who told me it was nothing much to worry about and if it gets worse then I will be referred back. The advice from him was to ease up on the pain medication if possible and find other ways to deal with my chronic pain.
Operation 5. By May 2016, we were once again going to re-insert a Mirena to try and help my issue, however, it didn’t want to go in, so I had my 5th Operation to have it inserted on the 2nd June 2016. (Even if it was only slightly effective for a couple months that gave us time to try figure out what we were going to do). I was using a lot pain medication still, and my bleeding was happening more than it wasn’t. Once again, I was anemic and needed to take supplements to help my iron. Luckily, I never needed a blood transfusion. I had honestly lost count of the amount of times I went to my doctor’s clinic and the emergency department. I couldn’t even tell you the names of all the different types of pain relief and contraception options I had tried. I was labelled as someone who just ‘wanted painkillers’ because the amount I was on would not fix my pain. I was anxious and depressed due to my declining health. I wanted to just stop taking everything, but the pain was so much I couldn’t even move. Still around 50 kilograms and I had now been on pain relief constantly for around 6 months.
Operation 6. At this stage I was feeling worse if anything, so I had my 6th operation to remove the Mirena once again, after failed attempts to remove it in the gynecologist unit.
Going in Circles: More Birth Control, More Pain and Problems and More Surgery
By September 2016, I had visited the hospital and doctors so many times I was known on a first name basis. By this time, I had begun to research treatment options extensively and spoke to multiple people, including my gynecologists and doctor which led to me to discussing a hysterectomy. By now, I was willing to try any option to rid me of this pain! After extensive discussion it was decided that I would just have my left ovary removed because that was the most troublesome. In September 2016, we scheduled a laparoscopic Left Salpingo- Oophorectomy (Left Ovary and Fallopian Tube Removal).
Operation 7. On the 12th of October (day after my 23rd birthday), I had my 7th Operation. During this operation they found another problem. This is when I was diagnosed with pelvic congestion syndrome/ Ovarian Vein reflux and was referred to another specialist- an Interventional Radiologist.
Pelvic Congestion Syndrome/Ovarian pain reflux
“Pelvic venous congestion syndrome is also known as ovarian vein reflux. It is a cause of chronic pelvic pain in approximately 13-40% of women. Chronic pelvic pain is pain in the lower abdomen which has been present for more than 6 months. Pelvic congestion syndrome is therefore a painful condition often caused by dilatation of the ovarian and/or pelvic veins (rather like varicose veins but in the pelvis) . Varicose veins are commonly seen in the legs when the veins become less elastic and the valves that stop the blood from flowing backwards stop working. This causes the blood to pool, due to gravity, causing enlarged, bulging and knotty veins. This is also what happens to the pelvic veins in pelvic venous congestion syndrome (PVCS). This pressure results in the pain of PVCS and may also cause visible varicose veins around the vulva, vagina, inner thigh, and sometimes, the buttock and down the leg (s).”
Things went well for a short while, but the pain just got worse again. Again, I was on a lot of pain killers. I was always forced to take Panadol first if I was admitted in the ED, before they prescribed anything else.
I was referred to another specialist – an Interventional radiologist.
I drove 5 hours to see an interventional radiologist as there were none locally who could take me in the public system. I was advised by him that I should have platinum coils inserted in my ovarian veins and a foam solution to kill off a bunch of other veins. They thought the PVCS could be the cause to my pain and this treatment could prevent me from getting anymore varicose veins. He told me I am lucky that my legs and vagina hadn’t been affected yet, and that I will need to keep an eye out for this in the future.
Operation 8. I had operation number 8 in March 2017. I wasn’t under general anesthetic this time. Just a “twilight sedation” where they used my main artery in my neck to insert the coils and other treatments. Thankfully, I was out of it for most of it!! I had multiple coils inserted and who knows how many other smaller veins were treated. They wanted me to stay admitted overnight but I couldn’t do it. I was actually a bit traumatized from the whole experience. I felt extremely alone and scared down in a “big city” hospital by myself. At one stage, they were so busy that the head of my bed was in a utility closet to get me out of the way. Unfortunately, this operation did not help my pain as much as I prayed it would. 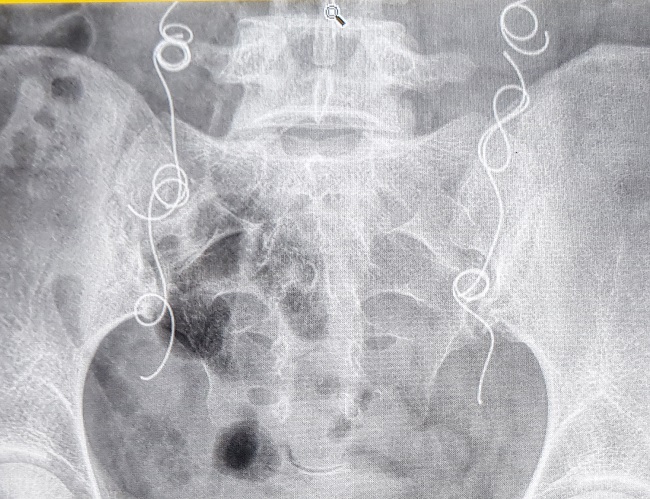
Chemical Menopause, Hysterectomy, and More Medications
I was at my wits end. I was breaking down emotionally, so I reconsidered a hysterectomy even though I was only 23 years old. The gynecologist I was seeing suggested that I go into chemical menopause before I had a hysterectomy so that I could see if it would benefit my pain. So, I did, I went on an injection called Zoladex. It causes chemical menopause and it’s actually used as a treatment for breast and prostate cancer. I was told not to research it but I couldn’t help myself.
I went to a regular GP appointment, but this time came out with more bad news. The results were that I have high cholesterol, which showed in a recent blood test. The doctor was a little confused because I didn’t have any of the major risk factors for high cholesterol. Turns out, that is what chemical (surgical or natural) menopause can do to one’s body. Now I had to add another specialist to the list of doctors and it meant another trip away. He told me if you have a hysterectomy and you take out your only remaining ovary, your cholesterol treatment will greatly differ”. He told me, “what would/could happen and that I must go back after my operation, but for now it was still untreated. So, with that news I felt like I needed to keep my only remaining ovary.
I was now seeing multiple professionals and had been seeing a gynecologist who made me regain hope. We talked about this operation multiple times over a long period of time and I was still suffering “chemical menopause” symptoms at that time, with my pain coming back worse the chemical menopause pellet started to run out. I was excited when the day finally came where I signed the papers to have a total hysterectomy. The advice I received was that I should make serious lifestyle changes to help my body. I was advised to do weight bearing exercises, quit smoking, go on Hormone Replacement Therapy and pray it doesn’t bring my pain back.
One thing that is still stuck in my mind is the line “this could take up to 10 years of your life”. I was in so much pain and I was sick of taking so much medicine that was making me sick in other ways. I really wanted to stop having operation after operation.
Operation 9. On the 2nd of August 2017, I had a total hysterectomy. I had everything except my right ovary removed. I must admit I felt strange, my belly felt empty, but I immediately felt like I had less pain.
It was the best thing I did for my pain. I felt like I had recovered from this operation fast and everyone (including myself) was amazed at how well I was doing physically afterwards. Ten days post op, I was able to stop all the pain medication I had been on! This was massive for me!!! No more pain killers! Or so I thought. My right ovary didn’t “wake up” after my hysterectomy and I began experiencing stronger menopause symptoms. I knew the obvious symptoms after having chemical menopause. This led me to the journey of figuring out and starting my first lot of Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT). I also came to the realization that it takes up to one year to fully heal from a total hysterectomy.
I must admit this affected me mentally and emotionally more than I thought it would. Some days are so bad, they scare me, other days I’m on top of the world. I think this definitely contributed to my mental health. One of the hardest things about having mental illness is getting up and putting on ‘you’re okay face’ every day. This isn’t makeup. This is the face where you put on a smile and say, “I’m fine”, or “I’m good thanks”. Its where you hope no one sees past your bulls**t smile because the moment they do you know you’ll break down and cry, but at the same time you just want someone to help you and help you not feel the way you feel anymore. Who knew hormones can mess with your head so much? Who knew hormones play apart in so many different things in your body?
Operation 10. On the 28th of June 2018, surgery number 10 happened. I had my right ovary removed. I had another cyst that was complex in nature and which was making my pain worst, contributing to me being back on pain killers again full-time. They also saw that the coil that was cut during my hysterectomy was exposed at the tip, so they trimmed this up as well. 
Surgical Menopause: Medicine’s Only Other Solution
After this operation, I “officially” entered surgical menopause. I have learnt what surgical menopause really is, and how much it differs from natural menopause. I also learned how under-educated people are regarding this condition, including some doctors and specialist. I didn’t know this was the journey I was going to be on for the rest of my life, however, I have learned that I am my only and best advocate. I still suffer from chronic pain every day, and now I have an added stress of menopause. All I can do is stay strong and true to what I know and keep fighting for myself and women like me. I will continue to try and get better health care for myself and I will not give up until I am satisfied, I have achieved this. This is not how my story ends.
Thank you for taking the time to read my story. Kind Regards, Jessica Poland (Firth). Queensland, Australia.
Share Your Story
If you have had similar experiences with hormonal birth control and/or medications and surgery, write and share your story on Hormones Matter.
We Need Your Help
More people than ever are reading Hormones Matter, a testament to the need for independent voices in health and medicine. We are not funded and accept limited advertising. Unlike many health sites, we don’t force you to purchase a subscription. We believe health information should be open to all. If you read Hormones Matter, like it, please help support it. Contribute now.
Yes, I would like to support Hormones Matter.
This article was published originally on November 29, 2021.