For as long as I can remember, I’ve always had an unusual partially feminine gender identity, but until recently I never consciously acknowledged it. Then, a couple of years ago I realised that, although at a conscious level I identify as male, my body language, my pattern of arousal and orgasm, and my instinctive social behaviour are all very much more like what you’d typically see in a woman rather than a man. In addition, I appear to be suffering from secondary hypogonadism (i.e. my brain regions that control hormones aren’t working correctly), and I have a “eunuchoid” body structure, which indicates that my testosterone production has been below normal all my life.
Is Being Transgendered Just One of Those Things?
Although it never became my career, as a student I excelled at both chemistry and biology, and I’ve retained an amateur interest in the sciences ever since. Most people seem to assume that being transgendered is “just one of those things”, but I resolved to use that background in science to try and figure out whether there was an actual physical explanation for it. Accordingly, I tried to discover as much as I could about sexual development in the unborn child, and the kinds of things that can go wrong with that process.
Sexual Blueprints
Our sex-determining chromosome, the Y chromosome, is far smaller than any of our other chromosome and only has a few dozen functional genes on it. Basically all the Y chromosome does is to tell your undifferentiated gonads to turn into testicles (without it they’ll turn into ovaries instead). All of the genetic blueprints for actually building a male or female body are located elsewhere in your genome, so everyone has the full set of instructions for both sexes.
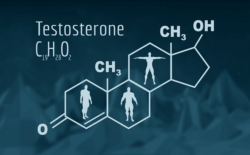
By default the “female” instructions are what get followed during fetal development, but if there’s testosterone present, the “male” instructions will be followed instead. Ordinarily this system works quite well, and you’ll develop as one sex throughout the pregnancy (which one depending on whether you have testicles churning out testosterone or not).
An Endocrine Disruptor
What appears to have happened in my case is that the pregnancy was no different from that of any other male baby, except that partway through the second trimester, something catastrophic happened that severely disrupted my endocrine system, so that for a few weeks I wasn’t producing any testosterone. Following that, my endocrine system recovered and everything went back to normal for the remainder of the pregnancy. The result is that I was built using the instructions for male development for most of the pregnancy, but during the time I wasn’t producing any testosterone, the instructions for female development were followed instead. That seems to have happened after all my physical development had completed, but very early in the process of wiring up my brain’s permanent structure (all the things that are affected seem to be associated with evolutionarily ancient parts of the brain, which points to the period of female development having happened early on in the process of wiring up my brain).
Based on when genital development takes place and when the process of building the permanent structure of the brain begins, I was able to work out that whatever it was must have happened somewhere around 16 or 17 weeks after conception, at or very soon after the time my mother would have first felt me moving inside her. Knowing what she was like when I was younger, my immediate thought was that she must have had a depressive episode, decided that she couldn’t cope with another child so soon after the first, and taken an overdose of something in an attempt to bring on a miscarriage.
A DIY Abortion That Didn’t Take
A bit of snooping on maternity forums soon revealed that the first thing most unhappily pregnant women contemplating a DIY abortion seem to think of is an overdose of contraceptive pills. I was able to subsequently confirm that my parents were using birth control pills for contraception at the time – the high dosage first generation ones. There was also something otherwise completely inexplicable that happened later in my childhood, which makes me think she must have been hiding a guilty secret along those lines.
My mother passed away in 2010, and in a way I’m glad that happened before I discovered any of this, because I would have been angry with her and she didn’t deserve that. She did her best to be a good mother to me and to all her other children, and I don’t hold her responsible in any way for what happened. I can’t blame my father either. He lost 3 brothers during his childhood and then his first wife died on their honeymoon, so I can understand why he became so obsessed with the idea of having a large family.
Brain Sexual Identity and DES
One further thing that made me think an exposure to artificial female hormones is the cause of my conditions was reading in the book “Brain Sex” about a pattern of behaviour commonly shown by teenage boys whose mothers were given treatment with a drug called diethylstilbestrol or DES in an attempt to prevent miscarriage . The boys in the study were typically very shy, socially withdrawn, had low self esteem, were regarded as sissies, bullied, ostracised by their peers, with no ability to fight back when attacked and no interest in sport. The authors of the book described it as “feminized behaviour”, and my teenage years matched it so closely it could have come straight out of my school report!
The main hormonal component of the contraceptive pills my parents were using is norethisterone acetate, a progestin, whereas DES is an estrogen. What estrogens and progestins both have in common is that they are female hormone derivatives, and are basically completely incompatible with masculinity. Both types of hormone have the ability to disrupt testicular hormone production at quite modest doses, well below those commonly used for medical treatment for women.
DES was for many years used to chemically castrate men suffering from hormone-sensitive prostate cancer, while progestins are commonly used for chemical castration of sex offenders and transsexuals. If they also suppress testosterone in a male fetus, then any use of them during a pregnancy of a male child carries a risk of creating a baby who developed as the wrong sex for part of the pregnancy. This is what I think happened to me, and to the DES sons.
For nearly two years I’ve been trying to find out as much as I can about DES sons, reading their personal accounts of how they’ve been affected and chatting with them online. Among the ones I’ve had contact with or whose life stories I’ve read, there seems to be a very high incidence of both intersex-related genital abnormalities and gender dysphoria. As a group they seem to commonly experience many of the same problems I have (a genital abnormality, feminized behaviour as a teenager, low testosterone and problems with hormones, gender variance). The key difference is that on the whole they seem to be far more psychologically female than I am (which is exactly what you’d expect, considering that their exposure was for a much larger part of the pregnancy than mine). I think it’s quite likely that for most of them, their testosterone production was completely suppressed and they were developing as female throughout the time their mothers were on the drug!
DES and all other estrogens were withdrawn from use in pregnancy 30 years ago, however, treatments for prevention of miscarriage, based on progestins rather than estrogens, continue to be used to the present day. One of these involves a progestin called hydroxyprogesterone caproate, given as a weekly intramuscular injection of either 250mg or 500mg, starting 16 weeks into the pregnancy – just around the time I think my hormone exposure occurred. The difference is that this treatment continues to be administered for the remainder of the pregnancy. If this drug does suppress testosterone production in a male fetus, then it’s hard to imagine a treatment better suited to creating as baby with a male body but a female brain! I’m fairly sure that if you gave an adult man 250mg per week of this drug, his testosterone production would be seriously impaired. Why wouldn’t the same happen to a male fetus?
Females Affected Too
In this article, I’ve only been looking at the effects of artificial sex hormones on a male fetus, however it’s likely that, under the right circumstances, a female fetus could be affected too. This could happen if the external hormone mimics the action of testosterone (e.g.progestin induced virilization), or if it disrupts endogenous hormone production in a way that causes excessive androgens to be produced (hyperandrogenism).
Postscript: This article was published previously September 2013.