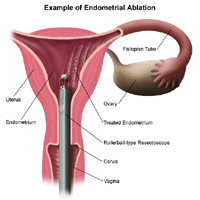
Endometrial ablation seems to be the latest “bag of tricks” in the treatment of women’s gynecological problems. It is an increasingly common procedure used to treat heavy menstrual bleeding. The procedure is premised on the notion that if the endometrial lining is destroyed – ablated – bleeding can no longer occur. Problem solved. But is it? Does endometrial ablation work? Does it resolve the heavy menstrual bleeding and prevent the “need” for a hysterectomy as it is marketed, or does endometrial ablation cause more problems than it solves? The research is sketchy, but here is what I found.
Short-term Complications Associated with Endometrial Ablation
For any surgical procedure there are risks associated with the procedure itself. Here are the short-term complications for endometrial ablation reported in PubMed: pelvic inflammatory disease, endometritis, first-degree skin burns, hematometra, vaginitis and/or cystitis. A search of the FDA MAUDE database included complications of thermal bowel injury (one resulting in death), uterine perforation, emergent laparotomy, intensive care unit admissions, necrotizing fasciitis that resulted in vulvectomy, ureterocutaneous ostomy, and bilateral below-the-knee amputations. Additional postoperative complications include:
- Pregnancy after endometrial ablation
- Pain-related obstructed menses (hematometra, postablation tubal sterilization syndrome)
- Failure to control menses (repeat ablation, hysterectomy)
- Risk from preexisting conditions (endometrial neoplasia, cesarean section)
- Infection
Long Term Complications of Endometrial Ablation
Endometrial ablation to block menstruation. In order to understand the long-term risks of endometrial ablation, one must understand the hormonal interaction between the uterus and ovaries. The endometrial (uterine) lining builds and sheds in response to the hormonal actions of the ovaries. Ablation scars the lining impeding its ability to shed. But ovaries continue to send the hormonal signals necessary for menstruation and the uterus attempts to function normally by becoming engorged with blood. The problem is, the blood has nowhere to go. It is trapped behind the scar tissue caused by the ablation. This causes all sorts of problems.
Retention of blood in the uterine cavity is called hematometra. If the blood backs up into the fallopian tubes it’s called hematosalpinx. Hematometra and hematosalpinx can cause acute and chronic pelvic pain. Some data suggest that about 10% of the women who have had endometrial ablation suffer from hematometra. The pelvic pain in women who’ve undergone both tubal sterilization and ablation has been coined postablation-tubal sterilization syndrome.
“Any bleeding from persistent or regenerating endometrium behind the scar may be obstructed and cause problems such as central hematometra, cornual hematometra, postablation tubal sterilization syndrome, retrograde menstruation, and potential delay in the diagnosis of endometrial cancer. The incidence of these complications is probably understated because most radiologists and pathologists have not been educated about the findings to make the appropriate diagnosis of cornual hematometra and postablation tubal sterilization syndrome.” Long term complications of endometrial ablation.
So although ablation can have the desired effect of reduced or even absent bleeding, it can be a double-edged sword. This relief from heavy bleeding may, in the long-term, be overshadowed by chronic, debilitating pain caused by the ongoing, monthly attempts by the uterus to build and shed the lining.
Ablation leads to hysterectomy in younger women. The younger a woman is at the time of ablation, the greater the risk of long-term problems that can then lead to hysterectomy. A 2008 study in Obstetrics & Gynecology found that 40% of women who underwent endometrial ablation before the age of 40 years, required a hysterectomy within 8 years. Similarly, 31% of ablations resulted in hysterectomy for 40-44.9 year old women, ~20% for 45-49.9 year old women and 12% of women over the age of 50 years required a hysterectomy after the endometrial ablation procedure.
Another study, reported a similar link between endometrial ablation and hystectomy. “On the basis of our findings one third of women undergoing rollerball endometrial ablation for menorrhagia (heavy menstrual bleeding) can expect to have a hysterectomy within 5 years. If the linear relationship noted during the first 5 years is extrapolated, theoretically, all women may need hysterectomy by 13 years.”
Post ablation tubal sterilization syndrome. A 1996 study of 300 women who underwent ablation found an array of pathological changes in the uterus including: hematosalpinx, endometriosis, chronic inflammation of the fallopian tubes, and acute and chronic myometritis. Eight percent of the women developed intense cyclic pain that necessitated a hysterectomy within 5-40 months post endometrial ablation.
Informed Consent That Isn’t
Recently, Hormones Matter has begun to explore the legalities of the medical informed consent, here and here. With all the adverse effects associated with endometrial ablation, especially the need for hysterectomy later, one must question whether women are informed about those risks. As I have found when investigating this topic, there are few long term studies on endometrial ablation. Many of the articles cited for this post come from paywalled journals that are not readily available to either the patients or the physicians – the costs are prohibitive for both. So it is not clear whether the physicians performing these procedures are aware of the long-term risks associated with ablation. And as one physician suggests, neither the pathologists nor radiologists responsible for diagnosing post ablation pathology are trained to recognize these complications. Without data or access to data and without training, one wonders whether it is even possible to have informed consent for a procedure like ablation.
You know the sayings “never mess with mother nature” and “you never know what you’ve got ’til it’s gone?” We need to heed those words at least when it comes to treatments that can’t be reversed or stopped! At the very least, we have to become thoroughly educated about the risks and benefits of any given medical procedure.
This post was published originally on Hormones Matter in May 2013.