I had the great pleasure of speaking to the Washington Alliance for Responsible Midwifery (WARM) recently about re-framing the concepts around maternal health and understanding the biases in medical research. One of the great questions that has been occupying my time lately is understanding how the frameworks for understanding medical concepts emerge. Shorthand: how do we know what we think we know? Below is an annotated and somewhat edited (for publication) version of the talk I gave. Enjoy.
What is Health?
When we think about health and illness, we all think we know what they are. We can see, touch, and measure health and illness in some very discrete and obvious ways. For example, in Western culture thin is good, fat is not good. If one is skinny, one must be healthy whereas if one overweight, one must be unhealthy.
Weight is a key parameter by which we all shorthand our assessment of health and illness. Indeed, weight, along with other visible qualities, like pallor and disposition, and some less immediately visible but easily measurable qualities like blood pressure, glucose, and other standard labs are key indicators that define health versus illness.
More often than not, however, our definitions of health and disease have been guided by external forces and systems of thought that are inherently biased, even though they claim the objectivity of science and evidence. These biases not only impact our views on health and illness, but in many ways, define what questions are acceptable to ask about health and disease.
Perinatal Mental Illness: An Entrenched Framework for Maternal Health and Illness
In my own research on perinatal mental illness, the prevailing wisdom was and still remains focused on questions that frame the discussion incorrectly. What I mean by that is the original ideas that initiated our notions of what causes postpartum mental illness – the change in progesterone and the estrogens – have become entrenched. Indeed, the ideas that the symptoms are a standard clinical depression or somehow a more serious degree of baby blues and tearfulness are well established.
When you think about pregnancy and postpartum, there are huge hormone changes, progesterone and estriol and estradiol being the most obvious, so it was reasonable to begin looking there. The problem is that, more than not, these hormones were never measured and when they were measured in association with depressive symptoms there were only weak correlations, if any correlations at all. After a while, one would think researchers would begin looking elsewhere, other hormones, other symptoms, but they didn’t. They just dug in deeper. The framework for perinatal mental health issues had already be set and to deviate was difficult at best, impossible for many.
I came to this conversation as a lowly graduate student. I thought, let’s look at other hormones and other symptoms, not just depression, and see what happens.
Lo and behold, other hormones were involved, as were other symptoms. But again, the framework was established and so the idea of expanding definitions of perinatal mental health, especially by someone who wasn’t a named researcher, was not a positive one.
The research was rejected over and over again and the politics of the maintaining the framework and only incrementally changing it were made quite clear to me, repeatedly. So much so that those controlling the dialogue were willing to dismiss where the data pointed to in order to frame the conversation as conventionally accepted – that progesterone and estrogens caused varying degrees of depression postpartum. Even though this made no sense logically; if this were the case, all women would be suffering and they were not. There was no supporting data, but it didn’t matter because as one reviewer commented about my research – ‘that is not the direction the hormone research is going’. So much for unbiased science.
This experience, added to my already disquieted disposition, led me to always dig deeper and look at the frameworks through which the research or ideas were being proposed. These are more philosophical questions, and yes, I have a degree in philosophy so I am naturally inclined towards these – but I think it is important to question how you know what you know and how others know what they know; those rules of knowledge determine, in large part, what can be known in a public sense, and will lead to tremendous insight in your practice – especially when what is accepted as standard clinical practice – doesn’t quite mesh with the patients in front of you. Dig and figure out what the framework was that developed those particular guidelines. Was it valid, was it commiserate with modern patients and current health issues or was it something that was skewed to begin with and has become increasingly more skewed – but we’re holding on to the practice anyway because it has become just the way we do things.
It’s a big topic – one where women and childbirth should play central roles but historically, we have been left out of the conversation.
Historical Frameworks for Maternal Health
To give you some context about how the frameworks impact clinical practice, let us consider the evolution of modern medicine. Historically, medicine has asserted the primacy of the physician’s ability to ‘see’ and thus, identify illness, over the subjectivity of the patient’s perspective about his or her health. So much so, that patients need not even speak unless spoken too and may only aid the physician to the extent they can answer those questions that the physician is interested in.
To say this has been a paternalistic approach is an understatement. Within this model of the physician as ‘seer’ and interpreter of signs and symptoms there is no room for the patient and his or her interpretation of the illness – especially her interpretation.
Despite its flaws, however, in many ways, this was a net positive for medical science. It allowed medicine to progress, for diseases to be systematically recorded and discussed – amongst other physicians of course – but still a critical step forward in medicine. Most importantly, this framework allowed medical science to begin developing treatments to specific diseases.
On the most basic level, one cannot manage a condition unless one can measure it, and to measure it, we have to be able to identify it and distinguish it from other diseases. And herein, lays much of problem with general women’s health and maternal health: what to measure, how to measure and what those measurements meant were largely decided by men who had no lived experience of ‘women’s health’ save perhaps, an observed experience with mothers, wives, sisters – which for all intents and purposes because of the political and cultural norms – women were separate.
So, the framework for women’s health, and most especially, maternal health was fundamentally flawed and inherently biased – from the onset. No matter that midwives had been delivering babies for generations and had built a wealth of knowledge – their influence, and power was usurped by physicians and that knowledge was summarily rejected. In its place practices and technologies that, in many cases, did not benefit women. Indeed, from the early 20th century onward, obstetrics considered childbirth a pathogenic condition requiring medical intervention.
Since within this model the patient had no role in either diagnostics or treatment consideration, but lay simply in front of the physician for him to ‘see’ and interpret the signs and symptoms of disease, the definitions of women’s health and disease and most especially maternal health – were obviously skewed. How could they not be, looking from the outside in – framing the questions from a distance?
Consider that not only were the very questions asked about women’s health defined by men, but the research subsequently, if it included women at all, was guided by the false presumptions that women were simply men with uteri.
And I should note, that women were summarily excluded from research until the late 1990s – so everything we know about medications prior to the 90s was based upon research with men, generally, young, healthy men at that.
It was believed and still held by many, that except for reproductive processes, men and women were fundamentally the same. Once we isolate those specific functions, there is no need to address women’s health any differently than men’s health. Or is there?
Is a Woman Simply a Man with a Uterus?
As women, I think we would all argue in favor of assessing women’s health differently than men’s health.
From a physiological and biochemical standpoint, male and female bodies are quite distinct, far beyond differences in reproductive capacity. In fact, these differences are exactly because of reproductive capacity and more specifically, the hormones that mediate those abilities.
If men and women are different – and of course they are – how do we know that what we know about women’s health is in fact accurate when most of women’s health research was defined by men? Do we really know anything, beyond the most basic assessments about women’s health?
I would argue that what we know or rather what we think we know, pretend to know, especially in western medicine, may not be accurate. The questions were framed incorrectly – from the perspective that women’s reproductive capacities, organs and hormones had no impact on the rest of her health. We could probably make the same argument for men, as their reproductive organs and hormones were dissociated from the rest of their health too – but because men controlled the research, defined the research, and importantly, had personal insight regarding their own physiological functioning, health knowledge is likely more accurate than what has been conveyed about women.
Shifting Frameworks Means Changing Definitions of Maternal Health
This isn’t just about differences in human physiology. If we dig into the framework by which we understand health, if we dig into the systems at play, we can see trends in how, as that power structure, as the lens, the framework for understanding health and disease shifts, so to do the definitions of health and disease and so too does the range of acceptable and unacceptable questions to ask.
If we look at recent decades with advent of HMOs and other payer contracts, along with the growth of hospitals, we see ever changing health and disease models. The model with physician as the central and all powerful seer and knower has shifted quite significantly by financial interests producing a factory like approach to healthcare.
With any factory, efficiency and cost cutting are key indicators of success. Instituting those efficiencies, however, largely removes the physician’s authority by shifting the primacy of his views towards the more efficient and less authoritative matching of symptoms to medications and billing codes. Cookbook medicine.
If symptoms reported by a patient don’t fit the ascribed to criteria, for all intents and purposes, the illness does not exist.
The physician, in many ways and recent decades, has become no more than a well-educated, technician answering not to his or her patients, but to the factory bosses – the insurers, the hospitals, and the regulators – the bean counters.
The physician is no longer central to medical science and clinical care. He/she is in many ways an administrator of care – a provider, not a healer, not even a scientists or medical researcher, save except to proffer funding from pharma or device companies.
Physicians have no power, no say in patient care, except to the extent that they can dot the i’s and cross the t’s according to billing codes. If their gut, or more importantly, if the data tell them that a particular treatment is dangerous, or conversely, is needed, but it doesn’t fall within the ascribed treatment plan, the physician has little recourse but to comply or risk losing his/her livelihood and, in more extreme cases, his/her reputation.
We see the barrage of reputation ending slanders hurled at physicians and researchers who dare to speak up and say that perhaps pesticide laden foods are not as safe as chemical companies make them out to be or that perhaps vaccines or other medications are neither as safe nor as effective as pharma and governmental institutions funded by pharma suggest. When physicians speak up, they risk their careers and reputation.
And while, you might be thinking there might be some positives to this shift, it is no longer such a paternalistic system where the physician has total power, in reality, this shift in healthcare towards efficiency still leaves women’s health high and dry and pushes the patient’s experience of his/her illness even further from the ‘knowledge base’ of western medicine.
Who Determines What We Know about Health and Disease? The Folly of Evidence Based in Women’s Health
So, back to this idea of frameworks, if neither the physician nor the patient is central to our definitions of health and disease, who is? Who determines what we know about health and disease?
In recent decades, clinical practice guidelines have emerged from what are called evidence-based claims. Evidence-based clinical guidelines sound like a perfectly acceptable and reasonable approach to medical science. Research should be done on clinical decisions and outcomes, the data paint a picture of the safety and efficacy of a particular treatment or approach.
Evidence-based is certainly far better than consensus based – which means the ‘experts’ agree that this approach or that approach is optimum – something that has been the norm in women’s health care for generations.
Indeed, most medications were (and are still) never tested on women, pregnant or otherwise, so clinical practice guidelines that involve medication use are developed by ‘consensus’ and what many doctors like to call ‘clinical intuition’.
But since the long-term effects of these intuitive decisions are rarely seen by the clinician whose intuition guided the initial decision, and rarely shared with others, the notion of consensus based medical decision-making becomes sketchy at best, dangerous at worst; unless, you are lucky enough to have a highly skilled and thoughtful practitioner who is able to discern and act upon the best interests of his patients, even if it means going outside the parameters of what the rest of the profession says is appropriate. Most of us are not that lucky and as women we are faced with a medical science that doesn’t quite fit our experience of health and disease.
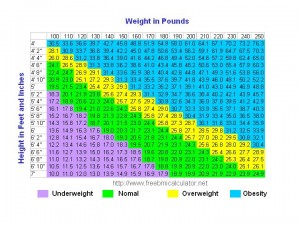
Of Weight and Health: The Obesity Paradox
If we go back to the shorthand measure of weight as a marker of health – how many of us tell ourselves if we just lose 10lbs we’ll be healthy. Every one of us, at some point or another has fallen into the weight = health trap. While it is true on extreme ends of the weight continuum that weight is related to disease, everywhere else and for everyone else, weight has little to do with ‘healthiness’. Weight loss has been noted to reduce blood pressure and type 2 diabetes, but the relationship is not as straightforward as it seems. Being of normal weight does not necessarily equal low blood pressure or increase your longevity. Weight is not correlated positively with mortality – death by heart attack or stroke. In fact, the relationship between weight and surviving a life-threatening disease is almost always inverse – the heavier you are, the better the chance for survival. Those fat stores come in handy when we are deathly ill.
Wait, what did I just say that? We should all go get fat and live longer – well, not really. Rather, I think we should look beyond weight as measure of health and to more appropriate measures like fitness, quality of life and the nutrient density of the diet. If you are eating well, active and feeling good, without any need for medication, then you are healthy.
Back to our evidence based approach – How can it be that the evidence behind what are gold standards of clinical practice be incorrect?
That is a big question that involves a little more background.
We all want our physicians to make healthcare decisions based upon the best available evidence and we can all think of ways that evidence is better than consensus, but each of these methods have their flaws.
Defining the Gold Standards in Clinical Care
When we look at the gold standards in clinical practice, those that align with evidence-based care, we have ask ourselves, from where did that evidence emerge, what were the variables, populations, and other factors studied and how were the outcomes determined.
How we define a good outcome versus a bad outcome determines how we design a particular study and what we results we will show.
Recall my example of the postpartum depression discussion – if we only ever measure progesterone and the estrogens (or don’t measure the hormones at all, simply assume those changes are at root of mood and psychiatric changes) and if we only measure depressive symptoms – then we have narrowed the framework such that we will only find associations or as the case may be – a lack of associations. And if there are no associations in the data – well then the disease must be made up and not real – all in the patient’s head.
The lack of questioning of one’s own biases, of the lens through which the research was designed or the parameters of what fits within that framework necessarily limits the understanding, making it easy to blame the patient. But if we step outside the framework, and listen to the patient’s experience, believe the patient experience and let it guide us, then we can break through the limitations of any particular framework and move science and healthcare forward. It sounds simple, and it is, but only if you recognize your biases and the biases of others and begin questioning, how you know what you know. And if that is not on solid ground, re-frame the questions.
Lies, Damned Lies and Statistics
You’ve all heard the phrase ‘lies, damned lies and statistics’ – it comes from the notion that research design, and particularly, the statistics can be swayed, intentionally or unintentionally, to prove or disprove anything. In medical science, this is especially true. Pick any medication for any disease and ask yourself how we determine whether it is effective or not?
First to mind, ‘it reduces symptoms’
Sounds reasonable – but dig deeper – which symptoms? All of the symptoms? Some of the symptoms?
And then if we dig even deeper…
Who decides which symptoms are important or even which symptoms are associated with a particular disease process? Over recent history, these decisions have been controlled by the pharmaceutical companies, insurance companies and hospital administrators – each with a specific bias and vested interest. The pharmaceutical companies want to sell products, the insurers and hospitals want to reduce costs and make more money. These should be counterbalancing agendas, but unfortunately they are not. The pharmaceutical companies have brilliantly controlled this conversation, defining not only the disease, but also, by controlling the research and defining the symptoms and prescribing guidelines. (I should note they also create new symptoms and disease processes to re-market old drugs to new populations; antidepressants for menopause, antidepressants for low sex drive in women, for example. The symptoms for both of these conditions are made worse by the very drugs being prescribed.)
If institutions or organizations with a vested interest are allowed to define the disease and the research by which a therapy is considered successful, how do we judge the validity of evidence-based guidelines?
Are the assumptions about the disease and the symptoms correct? Do these symptoms apply to all individuals with the disease or only those of certain age group? How about to women versus men?
Treatment Outcomes Determine Product Success or Failure
Take for example the case of statins, like Lipitor or Crestor, some of the most highly prescribed drugs on the market designed to lower cholesterol – because cholesterol was observed to be associated with heart disease in older men, particularly those who have had a heart attack previously.
Reducing cholesterol in this particular patient population might be beneficial to improved longevity (although, that has been questioned vigorously). However, does the rest of population benefit from cholesterol lowering drugs? It depends upon what outcomes are chosen in the research. If we, look at decreased mortality and morbidity as an outcome, then the answer to the question is no, statins are not good for the entire population with high cholesterol. A healthy diet and other lifestyle changes would be better.
Indeed, in women in particular, these drugs are dangerous because they increase Type 2 diabetes, increase vitamin B12 and CoQ10 deficiencies, among other nutrients (which initiates a host of devastating side effects), and most importantly, statins may increase the risk for heart attack and death in women.
So the drug promoted as one that prevents heart disease, may worsen it in women. Not really a tradeoff I would take.
This is problematic if one’s job is to maximize product sales. What do you do?
Let’s change the outcomes to the very simple, lowering of cholesterol. No need to worry about extraneous details like morbidity and mortality, keep it simple stupid.
Also, no need to compare the health of women versus men. Indeed, outcome differences between women men and women are rarely conducted, since statins decrease cholesterol in both women and men. Outcome achieved, evidence base defined, built and promoted.
A couple of points here…
He who defines the research design, controls the results. Across history, patients, especially women, have had no impact on these variables.
First it was the physicians, mostly male, and more recently, the product manufacturers have controlled the very definitions of health and disease, which in turn, determine treatments. To say evidence-based medicine is skewed is an understatement.
Now what?
While I’d argue that we have to re-frame the entire conversation about women’s health and include more voices in that conversation, voices that may not have been heard previously. I would also argue that we are never going remove biases from research and decisions about health and disease, but we can understand them and maybe even use them more effectively.
Revisiting the Foundations of Maternal Health – Enter Obstetrics
In maternal health, consider the Friedman curve and the failure to progress, though certainly not a product based bias as discussed previously, the Friedman curve, created in the 50s by a male physician at the height of hospitalized birth, where hospitals had a vested interest in understanding the progression of labor and its relationship not only to physician efforts, but time and outcome. For generations, this one study has guided OBs in their decisions to expedite labor – and as much research has found – has led the unheralded increase in cesarean delivery. Why?
One could argue that the study was flawed – it was – but most research is flawed in some way or another. I think the important thing is to understand the biases, how the question, and therefore, the answer were framed, and as importantly, who made the decisions about what was important in the framing of question?
Begin with the study population, was it skewed? Yes, it was.
For the Friedman study, more than half of the women had forceps used on them during the delivery (55%) and Pitocin was used to induce or augment labor in 13.8% of women. “Twilight sleep” was common at the time, and so 23% of the women were lightly sedated, 42% were moderately sedated, and 31% were deeply sedated (sometimes “excessively” sedated) with Demerol and scopolamine. In total 96% of the women were sedated with drugs. What might these drugs do to the progression of labor – stall it perhaps?
Digging deeper, consider the framework within which this study was conducted. Hospital births in the 1950s were predominantly drugged, sterile (or presumed sterile). Efficiency and scientific prowess were on the rise. Time was of the essence and there was very strong impetus to gauge decisions based upon the most advanced medical science – drugs, interventions – and an equally strong pull not to allow women to progress more naturally – because then science would not have intervened.
How did this one study become the guiding factor in obstetrical care? Why did we think that this particular study group was representative of the entire population of birthing women? The obvious answer was that women had no voice in this conversation or in the birth itself. It was medical science and intervention from a place of ‘all-knowingness.’
There was never any question that these results could be skewed, until recently. It was accepted, and perhaps the only reason questions have arisen, I suspect, is because of the links between the medical management of birth and the increasing rates of cesareans and maternal and infant mortality in the US over recent decades. Would this study have become so entrenched if the patients – the women – had a voice in the conversations about childbirth or the outcome was not so closely tied to hospital efficiencies? We’ll never know, but one could postulate that under different circumstances the study might have been framed differently and netted different results entirely.
Maternal Hypertension
Another, more recent example of how the framing of the question determines the conclusions of the research, involves how we view high blood pressure in pregnant women. Hypertension during pregnancy is dangerous for the mom – but what do we do? Treat it with non-tested anti-hypertensives, for which we know nothing about the potential side effects to the fetus short or long term ? Do we change diet? Do we simply monitor and hope for the best? What do we do? We don’t know. There is limited research on the topic, including on commonly used interventions.
With such limited research, I had high hopes for recent study, Less-Tight versus Tight Control of Hypertension in Pregnancy. It was a huge and well-funded study with a wonderful opportunity to determine the risks/benefits of anti-hypertensive therapy, but by all accounts, and in my opinion, it failed because the questions it asked were framed incorrectly. (Or were they? For pharmaceutical companies, the study was success. More on that in a moment).
That is, rather assessing the safety and efficacy of anti-hypertensive medications used during pregnancy (remember safety data for medication use during pregnancy is severely lacking), this study investigated a very narrowly defined and essentially meaningless question. The study asked whether controlling maternal blood pressure strictly within a pre-defined and arbitrary range of blood pressure parameters provided better or worse maternal or fetal outcomes compared to a more flexible approach that allowed broader range of accepted blood pressure metrics.
It did not analyze maternal or infant complications relative to particular medications to determine whether some medications were safer than others. It did not look at dose-response curves relative to those medications and outcomes or sufficiently address the role of pre-existing conditions relative to medications and outcomes. All it did, was ask whether or not managing maternal blood pressure more or less tightly with medications (that were not assessed in any meaningful way) was beneficial or harmful to maternal or infant outcomes. Since both groups of women were on various medications, varying doses and had a host of pre-existing conditions, the results showed that both groups had complications. It did not tell us which medications were safer, what doses of these medications were more dangerous or anything useful for clinical care. It just told us that anti-hypertensive medications during pregnancy, reduce blood pressure (we knew that) and cause complications (we knew that too). My review of the study.
Now, because of way the study was framed and especially how the conclusion was framed – that both tight control and loose control of maternal blood pressure show equal numbers of complications – the message will, and already has, become – blood pressure medications during pregnancy are safe.
- Medscape reports: Moms, Newborns Do Just Fine, Thanks, After ‘Tight’ BP Control in Pregnancy
- Contemporary OB/Gyn reports: Tighter prenatal hypertension control doesn’t result in larger babies, later births. Tight control of hypertension in pregnancy does not produce better perinatal outcomes or fewer serious maternal complications than looser control, according to results of an international randomized clinical trial.
- Science Daily reports: New research recommends treating elevated blood pressure during pregnancy.
The study found no such thing. In fact, the study found nothing really, but because of how it was framed it now becomes shorthand evidence of drug safety during pregnancy. Only those who read the full study with a questioning mind will know that this is not accurate. Most of the population, including physicians, will see only the shorthand PR surrounding the study and assume drug safety.
Conclusion
In conclusion – I want you to go back to practices and think about how you know what you know and if something doesn’t quite mesh – dig deeper – look at the framework from within which that guideline came to be. Look at the original research and decide for yourself.
I think it is time for women, midwives to have a much stronger voice in maternal health care, but to do that, we have to speak up and speak out and not accept the ‘gold standards of care’ just because they are the gold standards. While it is true, sometimes those standards will align well with maternal healthcare, other times, I think you’ll find that because of how the questions were framed, the solutions were skewed and do not match the reality of maternal health and disease.
Thank you.
We Need Your Help
More people than ever are reading Hormones Matter, a testament to the need for independent voices in health and medicine. We are not funded and accept limited advertising. Unlike many health sites, we don’t force you to purchase a subscription. We believe health information should be open to all. If you read Hormones Matter, like it, please help support it. Contribute now.
Yes, I would like to support Hormones Matter.
Image by StockSnap from Pixabay/
Tony Webster tonywebster, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
Originally published March 31, 2015.