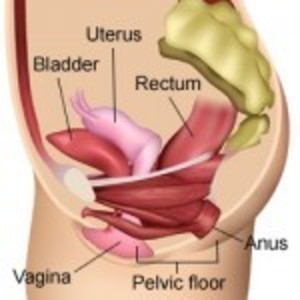
Since my last post in March 2013, after my second surgery for endometriosis I have been through hell and back. My endometriosis continued to spread and cause pain and my doctors all but ignored my declining health.
December 24th 2013 I wrote my surgeon a letter to express my discontent. I did not feel that I received the care I needed, especially from one of the physicians he had trained. I felt betrayed and was still suffering immensely; I was left to fend for myself. According to them, if I wasn’t willing to take huge doses of endometriosis, nerve or antidepressant meds, then I wasn’t worth their time. I was a lost cause and they effectively ignored me. I really felt lost in the Endo world once again.
When I wrote the letter to my physician, I was at a low point in my life. I hated my job; the stress was so high that I could barely cope. I was on and off medications prescribed by the pain clinic, in addition to those prescribed by my family physician. The side effects from all of these meds were so bad I could not function at work. I would cry at a drop of a dime. I was sick every day. I had to deal with stressful things that I should not have been put in the position to do. I felt like I was losing my mind.
Unexpected Compassion
I can’t remember the exact date, but sometime late January 2014 I got a phone call that changed my whole life. I wasn’t expecting anything, just to vent my frustrations. The nurse intern to one of my original surgeons called me. She said that she had spoken to the surgeon and was told to call me to say that “there seemed to be some misunderstanding” regarding my care. Umm no; there was no misunderstanding, as far as I could tell. The care was bad and they disregarded my continued pain.
She wanted me to come in for an appointment. I was hesitant. I had seen this physician so many times and left his office crying on many occasions over the last three years that I could not see willingly enduring any more appointments. How could I withstand yet another appointment where I was pushed to take more drugs that did nothing to alleviate the pain, while making me suicidal and depressed?
I eventually decided to go to the appointment, because in Canada we have no endometriosis specialists. He is the only one.
I had an appointment with this physician the second week of February. I saw my GP a week before. I felt like I was losing my mind. I needed something to help. She suggested Prozac. I was reluctant, but desperate. I could barely get out of bed, I felt disassociated from my body and felt that I just wanted to end everything. I was suicidal and psychotic.
The following week, I saw my surgeon and he did indeed try to push me onto some fancy, new med that was used for fibroids but was started to be used for endometriosis as well. I pretty much tuned him out. None of these meds work and the side effects are often worse than the original disease. I felt that no matter what I said, he would not listen. I started to cry. It was at this point, his nurse intern, my angel, spoke on my behalf. I am not sure whether it was her job to advocate, but she did and I am forever grateful. From our conversations on the phone and prior to this appointment, she knew what I wanted and expected to have happen. She wasn’t going to let me leave that office without having been heard. When I stuttered or began crying, she stepped in and said what I wanted to say. She held my hand, gave me tissue and had the empathy of someone you would expect to have when they too have experienced life with endo. It was a first for me, her compassion. In all of my 24 years of dealing with physicians and endometriosis, she was the first caregiver who expressed compassion.