I had an ablation at age 48 after heavy and debilitating bleeding that was robbing me of my life. At age 58, I had a hysterectomy where the cervix was also removed. Before the ablation, I spent half the day in the washroom changing pads and I was undergoing a demanding home renovation at the same time. It was hard to meet with construction contractors while blood would start gushing out of me at any given time. The bleeding made it very difficult to give important issues my undivided attention. Long story short, I had the ablation and it did solve the problem of the bleeding but intercourse became impossible. It was agony, so I gave it up. Even when I had to have a trans-vaginal ultrasound the instrument would not fit past 1-2 inches so it could not be done. I was never warned about these consequences. In spite of all that, the relentless bleeding was still the greater of the two evils.
I live in Canada and I must say I was not encouraged to have a hysterectomy for the bleeding. The family doctor would do nothing but prescribe hormones of some kind for 6 months, which not only did nothing for the bleeding but they had side effects on top of it. The hormones made me feel nauseous and bloated while I prayed for the bleeding to stop. The gynecologist that did the ablation and myomectomy for the large fibroid that was supposedly the cause of the bleeding only gave me one clue about the problems I might encounter. He commented several times that average age of menopause is 51 and since I was 48 it would mean that if I was intended to start menopause at the average age, this procedure would mean that I would start three years earlier. I didn’t think menopause would shrink the length of my vagina and turn my insides into “sandpaper” as was described by my longtime partner. I still don’t understand how that happens because of an ablation but any insights would be welcome.
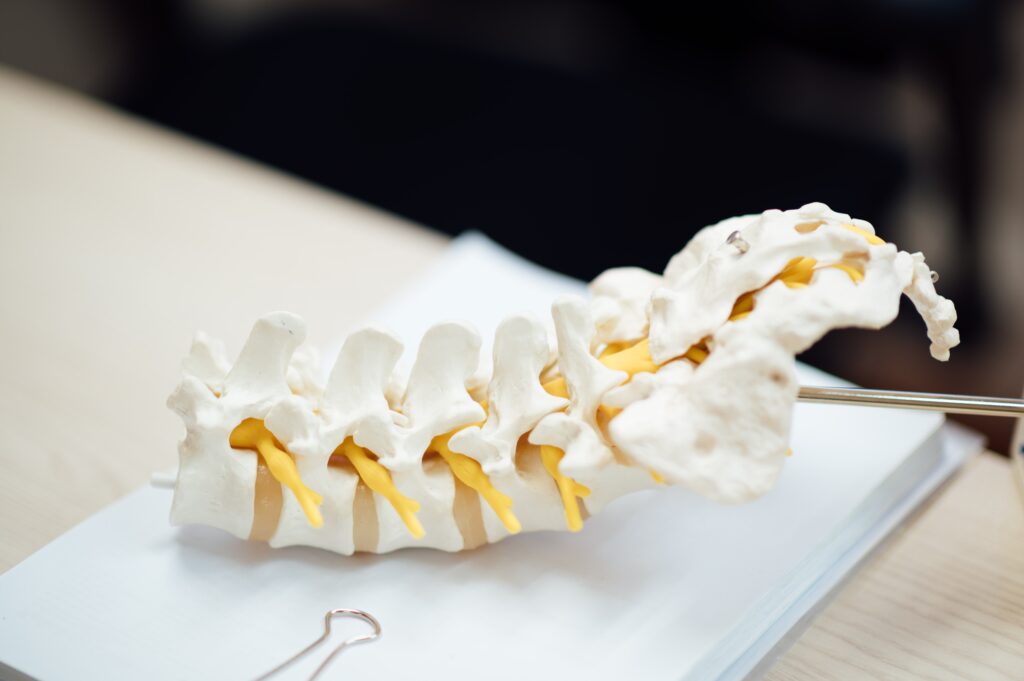
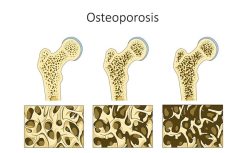
New Onset Osteoporosis and Scoliosis
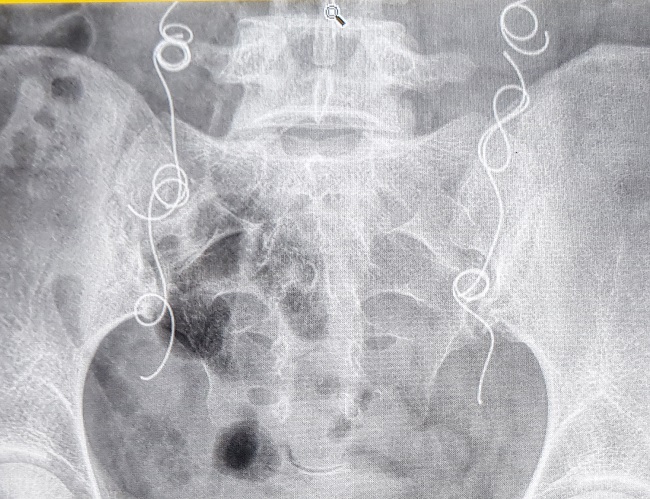
What I found interesting after reading the comments on the ablation and hysterectomy topics is that without the ligament cutting of the hysterectomy, I started to get the same effects after the ablation. First, I noticed that one side of my waist was not indented like the other one. I went to a physiotherapist thinking I needed special exercises. She gave me various exercises to do, which didn’t work because she was not keen enough to notice that I actually had the symptoms of lumbar scoliosis. None of the posts I read mentioned any experiences where an ablation could be connected to scoliosis or osteoporosis and so I am very curious to know if others have noticed if, not long after the ablation (within 12-18 mos.), their bones became weaker and osteoporosis and scoliosis set in?
I had never associated the ribs dropping to the hips with the hysterectomy because I already had this happen before the hysterectomy and after the ablation. All along I have been blaming it on the lumbar curve in my spine and the low bone density. What I found unusual is that at age 50 my family doctor sent me for a BMD x-ray (my first) and when she got the results she did not alert me that I had osteopenia or that I should be upping my calcium and Vitamin D intake. Because this doctor minimized the concerning results I had a false sense of security that all was well. I was totally unaware that behind the scenes my condition was deteriorating into moderate to severe osteoporosis or that I had a lumbar curve of over 30 degrees. It took me FIVE years to get the miserable truth with the next BMD at 55.
Three Inches Shorter but Taller in Wisdom
In Canada a woman is entitled to a BMD every 5 years if they are in the normal range. Not only did this family doctor not warn me about fighting the osteopenia, she could have sent me back for another BMD much sooner because I was not in the normal range. In fact it was MY idea to get the BMD at 55 just because I was eligible again. I was completely unsuspecting of the gruesome truth about my condition. By this point, all of the same skeletal changes that those who have had hysterectomies describe had manifested. I can’t help but wonder if there is possibly a connection between ablation and bone weakness leading to osteoporosis and scoliosis providing yet another way for the spine to compress? Any information or similar stories would be gratefully appreciated and any questions someone might have of me if I left anything out would be more than welcome. It is unfortunate that a genuine attempt to solve one health problem would lead to so many unwelcome and unexpected changes to our bodies and our peace of mind. The only good that has come from this is that I finally found this website.
We Need Your Help
More people than ever are reading Hormones Matter, a testament to the need for independent voices in health and medicine. We are not funded and accept limited advertising. Unlike many health sites, we don’t force you to purchase a subscription. We believe health information should be open to all. If you read Hormones Matter, like it, please help support it. Contribute now.
Yes, I would like to support Hormones Matter.
Photo by CHUTTERSNAP on Unsplash.