I am not a big fan of metformin (Glucophage). My disdain for metformin stems not from its efficacy. Metformin is quite adept at lowering blood sugar. In that sense, it is a medical marvel. Consider a pill that will ensure that no matter the individual’s intake of sugar, blood glucose measurements will magically fall within a normal range. What a wonderful invention – to have one’s cake, eat it too, and all the while, maintain normal blood sugar – who wouldn’t want that?
Alas, however, like all magic tricks, when the sleight of hand is revealed, the luster is lost. In the case of metformin, the underlying prestidigitation is not so magical after all. Metformin, like other wonder drugs, treats a symptom of a much greater problem; a symptom that in reality is just a visible sign of a necessary and protective innate process designed for cellular survival. The symptom is insulin resistance, the problem is too much dietary sugar and too few nutrients – an insidious form of high-calorie malnutrition that at once overloads cellular and mitochondrial processing capacities and starves the cells of critical nutrients.
Nutrients – They’re Necessary
A little-appreciated fact in modern medicine, vitamins and minerals power all of the machinery involved in cell function and in mitochondrial energy production. No nutrients, no energy, cellular starvation (even in the face of weight gain), inflammation, dysfunction, and ultimately, death. In the face of too much sugar and not enough nutrition, insulin resistance seems perfectly logical. If cellular fuel is waning, why not keep a little extra floating around, but since the apparatus to process said sugars is crippled, we have to turn down the intake valves. I would argue that it’s not obesity causing insulin resistance, after all not all overweight folks have type 2 diabetes, and not all insulin-resistant diabetics are overweight. It’s the damned sugar and lack of other nutrients initiating insulin resistance. Both the insulin resistance and fat storage are survival mechanisms; ones that ultimately have pathological consequences, but survival mechanisms nevertheless. In fact, folks who are diabetic and overweight have a lower all-cause mortality rate than those who are diabetic and thin.
If the problem is high-calorie malnutrition, which manifests as elevated blood sugar and in many cases, increased fat storage, wouldn’t the more prudent solution be to rectify the problem, to cease sugar intake, and address the nutrient deficiency? Wouldn’t that unwind the damage and heal the body? I think so, but alas, that’s not what we do in modern medicine. No, we don’t correct the problem, we treat the symptom(s) and then we revel in all the cool mechanisms we can interrupt, never considering the bigger picture.
Metformin Usurps Cell Signaling
Metformin bypasses our cells’ innate response to too much of anything – downregulation or desensitization – by overriding the communication systems that control these functions. In this case, metformin becomes the signaling molecule that tells the liver if and when to release glucose into the bloodstream. From an engineering standpoint, it’s a fantastic workaround. No need to address the core problem, just rewire the communication and continue on as if nothing is wrong. The added bonus is that for all intents and purposes, it works. Blood sugar declines, as does some of the pathology associated with elevated blood sugar. A medical marvel, right?
Well, not so fast. It just so happens that we need those pesky nutrients to function and to survive. When we give metformin to individuals who are already in a state of malnutrition, we are effectively ignoring and extending the underlying deficiencies that initiated the insulin resistance in the first place. More importantly, and this is something that is missed almost entirely in western medicine, we are adding to the metabolic mess a chemical that directly leaches a whole bunch of nutrients on its own (which further disables cell function, increases insulin resistance, increases fat storage in the long term and all of the associated pathologies we have come to know and love). Furthermore, we’re disrupting energy metabolism – energy that all cells need to function – and while that may quell some pathologies in the short term, in the long term, we’re all but guaranteeing a progressive decline into ill-health, despite the cheerleading that suggests otherwise.
We Get It. Metformin Treats a Symptom Not the Root Cause. So What?
Why am I blustering on about metformin now, when I have done so on several occasions previously (here, here, and here)? Well, an emerging body of research is showing yet another set of mechanisms by which metformin derails health. It turns out, that in addition to depleting vitamins B12 and B9, which are responsible for 100s of enzymatic reactions and particularly important in central nervous system function including myelination (how many cases of diabetic neuropathy or multiple sclerosis are really vitamin b12 deficiency?) and tanking CoEnzyme Q10 which effectively cripples mitochondrial ATP production in muscles (and likely exercise capabilities) with the resultant loss inducing a whole host of pathological processes (muscle weakness, cognitive decline among a few), metformin also blocks vitamin B1 – thiamine – uptake by multiple mechanisms. And for kicks and giggles, it appears to interfere with the body’s innate toxicant metabolism pathways, the P450 enzymes, rendering those who use this drug less capable of effectively metabolizing a whole host of other medications and environmental toxicants.
Thiamine is Critically Important to Health
For those of you who don’t read our blog and/or are not familiar with thiamine and thiamine deficiency, let’s just say, thiamine is the granddaddy of nutrients, an essential cofactor at the top of the fuel processing pyramid. Without thiamine, food fuel from carbs and, to a lesser extent, fats cannot be converted into ATP. With declining fuel sources, mitochondrial functioning degrades as well and all sorts of diseases processes ensue.
Sit with that for a moment. We’re giving folks who already have an issue with converting foods to energy and who are already very likely nutrient deficient, a medication that blocks the very first step in that conversion process. Since metformin also blocks the lactate pathway and acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase (an enzyme necessary to process fatty acids into fuels), blocking thiamine effectively shunts the mitochondrial input pathways. Mind you, this is in addition to blocking the critical electron transport functions – via CoQ10 – found at the back of ATP processing. Talk about an induction of energetic stress.
So What If a Few Vitamins Are Depleted?
I bet you’re thinking if these nutrients are so important and metformin is so dangerous, why isn’t metformin more toxic? After all, metformin has been on the market for over 50 years, is considered the first line of treatment for type 2 diabetes, and just about every research article published on this drug begins with a blanket statement that metformin has an excellent safety record.
Why, indeed? Let us consider what constitutes a safe drug?
In modern medicine, the notion of drug safety and toxicology are equated with acute reactions. For decades, we have been operating under the false assumption in medical and environmental toxicology that if something doesn’t kill us immediately it must be safe (and the equally false assumption that toxicological responses are necessarily linear). Many drugs (and environmental toxicants) are much more subtle in their damage. They disrupt systems that, in many cases, have the capacity to compensate, at least for a period of time and until a critical threshold is met. Mitochondrial energetics is one of those systems that is remarkably resilient in the face of a myriad of stressors, sometimes taking years for the damage to be recognized. With nutrient deficiencies, in particular, compensation is aided by continuously changing environmental and lifestyle considerations. Sometimes we eat very well and other times we don’t; sometimes life is good, other times, it is not. Stressors vary.
Nutrient Deficiencies Wax and Wane
With nutrients deficiencies, especially essential nutrients that require dietary intake, there can be waxing and waning of the symptoms that these deficits evoke as diet and other variables change. It’s not until one reaches a critical threshold that the deficiency is recognized if it is recognized at all. With thiamine deficiency, in particular, animal research suggests the threshold for severe symptoms may be as high as 80% depletion. Imagine a system that can maintain life in the face of up to an 80% deficiency. That is remarkable.
Symptoms of severe thiamine deficiency include those associated with a condition called Wernicke’s Encephalopathy, a serious and potentially fatal medical emergency with neurological and cognitive impairments, oculomotor and gait disturbances, and cardiac instability. With milder deficiencies, however, we see things like fatigue, muscle pain, mental fuzziness, GI disturbances, autonomic dysregulation, and a host of symptoms that can easily and incorrectly be attributed to other conditions and/or modern life in general.
Interestingly, once thiamine depletion reaches that critical threshold, it doesn’t take much thiamine to begin seeing improvement in the symptoms. In those same animal studies mentioned above, it took an increase of only 6% of the total thiamine concentration to begin the improvement. So with a change from 20 to 26% of recommended thiamine concentration, symptoms begin to dissipate, at least temporarily. Sit with than one for a moment – what a remarkable bit of resilience. It takes a full 80% reduction in thiamine stores before serious symptoms are recognized but improvement begins with only an additional 6% – when the system is still depleted by 74%.
Given the metabolic capacity to maintain survival in the face of all but critical deficiencies, it is easy to see how and why blocking these nutrients would not be considered dangerous or at least obviously so. The decline is so gradual in most cases, and likely waxes and wanes, that it becomes near impossible to attribute symptoms and underlying nutrient deficiencies to the offending medication(s). Unfortunately, just because we don’t recognize those patterns, doesn’t mean that they do not exist.
How Metformin Blocks Thiamine: The Technicals
Backing up just a bit, it is important to understand the mechanisms by which metformin reduces thiamine. When metformin is present, a set of transporters that normally bring thiamine into the cell to perform its task as a cofactor in the machinery that converts carbs to ATP, brings metformin into the cell instead, replacing thiamine altogether. The transporters involved are the SLC22A1, also called the organic cation transporter 1, [OAT1], and the SLC19A3. Conversely, when metformin is not present or at least not overwhelming all of the transporters as it is during the initial phases of absorption post intake, thiamine becomes available for transport. Since these transporters are not completely and continuously blocked (and there are other thiamine transporters), thiamine uptake occurs, just not continuously and just not at full capacity. This may be one reason why metformin is not as acutely damaging as some of the other drugs in its class, but make no mistake, it is still dangerous. Thiamine deficiency is deadly. With the right combination of thiamine blocking variables (other medications/vaccines block thiamine as well), thiamine concentrations can tank and even if the thiamine concentrations hover at a subclinical deficit, the likelihood of chronic illness is high.
Thiamine and Diabetes: Connecting a Few More Dots
A little over a year ago, I stumbled upon some research showing a high rate of thiamine deficiency in individuals with both type 1 and type 2 diabetes (75% and 64%, respectively). I wrote about that research in Diabetes and Thiamine: A Novel Treatment Opportunity. According to several studies, diabetics appear to excrete higher amounts of thiamine than non-diabetics. The research attributes this to either poor kidney reabsorption and/or mutations in the thiamine transporter genes that prevent absorption. None of the research detailed the medication usage of the participants, but one might expect a good percentage of the type 2 diabetics were using metformin. It seems reasonable that if metformin supplants thiamine uptake via the thiamine transporters mentioned above, then the body would excrete the unused thiamine, leading to a higher rate of thiamine excretion than observed in non-diabetics and a higher rate of thiamine deficiency in diabetics versus non-diabetics. Based upon this, additional clinical research has shown that thiamine supplementation normalizes, the aberrant processes activated by sustained hyperglycemia including:
- High dose thiamine (300mg/day) reduces the biochemical stress of hyperglycemia in human subjects.
- Thiamine can prevent and/or offset incipient vascular damage in diabetic patients.
- In rodent models of Type 1 diabetes, thiamine transporters have been identified and emerging research shows that thiamine moderates pancreatic insulin secretion significantly.
Metformin, in treating a symptom rather than a root cause, is likely exacerbating, and perhaps even initiating, some of the very disease processes that it is intended to prevent. Although metformin is not often acutely toxic, the underlying mechanisms manipulated by this drug suggest that it is likely to induce and not prevent, as is so frequently suggested, chronic illness. From my perspective, that makes metformin a very dangerous drug.
We Need Your Help
More people than ever are reading Hormones Matter, a testament to the need for independent voices in health and medicine. We are not funded and accept limited advertising. Unlike many health sites, we don’t force you to purchase a subscription. We believe health information should be open to all. If you read Hormones Matter, and like it, please help support it. Contribute now.
Yes, I would like to support Hormones Matter.
This article was published originally on Hormones Matter on February 16, 2016.

























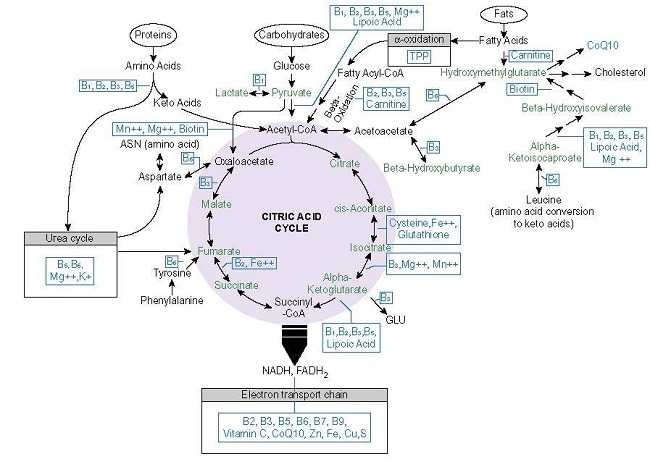 A few things should be pointed out. First, while these nutrients are required by everyone for proper mitochondrial functioning, not everyone needs to supplement with each one, or even sometimes any of them, although that is becoming increasingly rare with modern dietary patterns. Secondly, notice how many times and where vitamin B1 (thiamine) appears in this chart. It is at the entry points of the entire system and at various junctures throughout. This suggests that among all of the nutrients required for healthy mitochondria, thiamine is particularly important. Unfortunately, it is the one nutrient that is so often ignored or missed in testing. Indeed, that is why we wrote the book. Thirdly, notice how many vitamins are required to process the food we eat into ATP. Contrary to popular opinion, we need more than simply empty calories. For the foods we eat to be converted into ATP, there are multitude of vitamins and minerals required that may or may not be included in sufficient density with the macronutrients we consume daily. Finally, not discussed in this chart, but discussed in great detail in the book, synthetic chemicals, whether in form of pharmaceuticals, industrial, environmental, or food production, damage the mitochondria. Some deplete nutrients directly, while others damage aspects of mitochondrial functioning that necessitate increased nutrient density for the enzyme machinery to work. Of course, underlying all of this, are the genetic variables that each of us brings to the table. These influence how well or poorly we metabolize any of these nutrients from the get-go. All of this combines to make nutrient therapies complicated.
A few things should be pointed out. First, while these nutrients are required by everyone for proper mitochondrial functioning, not everyone needs to supplement with each one, or even sometimes any of them, although that is becoming increasingly rare with modern dietary patterns. Secondly, notice how many times and where vitamin B1 (thiamine) appears in this chart. It is at the entry points of the entire system and at various junctures throughout. This suggests that among all of the nutrients required for healthy mitochondria, thiamine is particularly important. Unfortunately, it is the one nutrient that is so often ignored or missed in testing. Indeed, that is why we wrote the book. Thirdly, notice how many vitamins are required to process the food we eat into ATP. Contrary to popular opinion, we need more than simply empty calories. For the foods we eat to be converted into ATP, there are multitude of vitamins and minerals required that may or may not be included in sufficient density with the macronutrients we consume daily. Finally, not discussed in this chart, but discussed in great detail in the book, synthetic chemicals, whether in form of pharmaceuticals, industrial, environmental, or food production, damage the mitochondria. Some deplete nutrients directly, while others damage aspects of mitochondrial functioning that necessitate increased nutrient density for the enzyme machinery to work. Of course, underlying all of this, are the genetic variables that each of us brings to the table. These influence how well or poorly we metabolize any of these nutrients from the get-go. All of this combines to make nutrient therapies complicated.